|
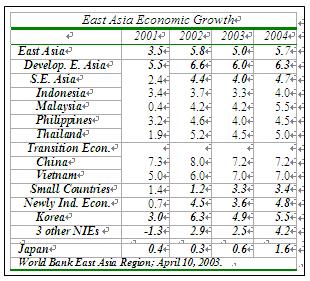
External shocks such as the Iraq crisis and the outbreak of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) have put East Asia in a troubled and uncertain environment, despite strong growth of nearly 6 percent over the last year. Given the range of uncertainties, the World Bank’s new update on East Asia projects that growth will fall by almost a percentage point in 2003, to 5 percent, before rebounding in 2004.
“Although this growth projection is less than what was initially hoped for, the East Asia region has fundamental strengths that should enable it to withstand these short-term shocks, and grow faster than any other region in the world,” said Vice President for East Asia and the Pacific Mr. Jemal-ud-din Kassum at today’s launch.
Addressing the Impact of SARS
With SARS having replaced the war in Iraq as the region’s most pressing concern, the report addresses policy implications of SARS, beyond the obvious need for stringent public health measures to control the spread of the disease. “Since the short run economic impacts are almost entirely based on public fears, information policy will play a critical role. Frankness and transparency in public information, then, will be critical in building trust and minimizing the economic costs of SARS,” Mr. Kassum said.
Although addressing the economic impact of SARS is unusually difficult, Mr. Kassum said that most projections show worst-affected industries in the short run are likely to be service industries based on face to face interaction between service providers and customers – such as tourism, business travel, transportation, and retail sales. In most-affected areas like Hong Kong, retail sales are already depressed – Hong Kong's Retail Management Association said in early April that retail sales had plunged between 50–80 percent since the outbreak of SARS last month. With a scenario based on assumptions about how much tourism and other activities will fall, and on how important tourism is to each economy, the report estimates the impact effect of SARS could reduce regional growth by 0.3 percentage points – while additional multiplier effects could double that figure.
“Like the Iraq crisis, SARS is in principle a temporary shock – although there is a great deal of uncertainty as to how large the SARS crisis will be in the end. Countries with high foreign reserves and a decent fiscal position may well be inclined to consider carefully designed policies that support economic activity during the shock,” said Mr. Kassum. He noted that the region as a whole has run large current account surpluses and built up regional foreign exchange reserves totaling nearly $800 billion dollars – about 30 percent of regional GDP – and therefore, most of the larger economies should have less difficulty in financing the adverse shocks of 2003.
Future Outlook: Strengths of the Past Help Region
The report cites a number of reasons for an overall optimistic outlook, including: modestly stronger OECD growth and world trade this year; higher world agricultural prices boosting incomes in South East Asia, especially in rural areas; falling spreads on high yield debt suggesting that world capital markets are looking on emerging economies with a more favorable eye; and the build up of high levels of foreign reserves in the region. Furthermore, the Iraq war turned out to be short, and many of the worst predicted effects did not materialize. Oil prices have receded from their peaks and are expected to fall further.
Commenting on further reasons for optimism about East Asia’s growth prospects was Mr. Homi Kharas, Chief Economist for East Asia and the Pacific Region. He said that the wide array of reforms undertaken by countries since the crisis have contributed to a gradual improvement in the profitability, balance sheets positions and resilience of banks and corporations in several countries. Stronger flows of consumer and housing credit have helped underpin stronger household consumption and housing construction. “SARS may have a severe effect over the short-term, but it is unlikely to stop the discernible underlying trend towards a gradual strengthening of East Asian domestic demand and activity.”
Mr. Kharas continued, “In a slightly longer term perspective, the last year saw a rapid expansion of East Asian intra-regional trade, in particular in East Asian trade with China, which is increasingly focused on trade in ‘high tech’ parts, components and products. Such trade is likely to enhance productivity among participants.”
Addressing the “China Challenge”
While China is one of the epicenters of the SARS outbreak, it is still generally expected to grow at robust rates. “The ‘China Challenge’ is not only a matter of coping with competition from Chinese producers in one’s home market or foreign markets, but also of seeking out and exploiting fast growing opportunities in the major trade and production hub emerging in China,” commented Mr. Milan Brahmbhatt, Lead Economist and principal author of the report. Exports to China from eight other East Asian countries rose 35 percent in 2002, contributing 37 percent of their total export growth, while the growth in trade among these eight countries themselves contributed another 29 percent.
“A key consideration for China this year,” said Deepak Bhattasali, Chief of the Economics Unit and Lead Economist for China, “is the management of the macroeconomic stimulus program. Prior to SARS, there was a feeling that China was growing strongly and the time was right for fiscal consolidation--easing fiscal stimulus spending and focusing again on effective development-oriented spending. Now, depending on how the economy performs, the need to continue to support consumer spending in the economy may re-emerge.”
Recent studies suggest that China is drawing in imports on the basis its own domestic demand, as well as inputs for the production of its exports. Strong domestic demand in China may therefore be providing a partial buffer against recession or slow growth in the rest of the world.
Addressing Poverty
East Asia’s poverty numbers continue to fall, with the number of poor measured at $2 a day level dropping by over 50 million to 724 million in 2002. Equivalently, the poverty rate at $2 a day level fell to about 40 percent, its lowest ever level, down from 43 percent in 2001. Robust poverty reduction was underpinned by better rural income gains in several countries – most notably China, supported in part by higher primary commodity prices. Despite a slower pace, economic growth should be sufficient to secure a continued fall in poverty in 2003, the report says.
Looking beyond this, the longer run problem of rural poverty will mainly be solved by the movement of population to more productive jobs in cities. A Special Focus on East Asia’s Urban Transformation in this report discusses these issues in depth.
Grappling with Challenges of Urbanization in East Asia
East Asia’s economic future depends on its urban areas, which are expected to contribute at least 70 percent of the region’s growth in the next twenty years. Cities are the main locus of globalization, the main centers for production of internationally traded goods and services and for location of foreign investment. The economic, demographic, and governance transitions associated with urbanization offer extraordinary opportunities for increased incomes and improved prosperity, but they also pose a challenge of unprecedented proportions for East Asia’s urban managers.
In the first quarter of this century the region’s urban population is set to grow by roughly half a billion people. If not properly managed, urbanization can take place in ways that exacerbate environmental damage, congestion, lack of basic services, ill health and insecurity. Growth strategies, poverty reduction programs, and infrastructure and environmental programs are now perhaps more vital at the city level than at the national level. Urban governments, many of them recently unshackled by new decentralization policies, are scrambling to meet these diverse demands. East Asia’s Urban Transformation reviews the long-term trends affecting cities in East Asia and their implications for urban policy and management, and offers recommendations for action.
(China.org.cn April 24, 2003)
|

