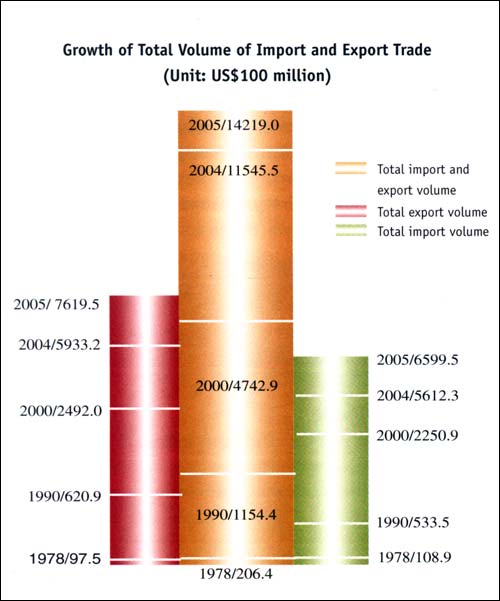
In 2004, China's commodity import and export volume ranked third in world trade, compared to 32nd place in 1978, 16th in 1990, and 8th in 2000. In 2005, the total amount of commodity import and export was US$1,421.9 billion, a 23.2 percent increase on 2004. At present, more than 220 countries and regions trade with China. Mainland China's 10 major trading partners are: the European Union (EU), the United States, Japan, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, ASEAN, the Republic of Korea, Taiwan Province, Russia, Australia and Canada.
On July 1, 2004, China began to implement the newly edited Foreign Trade Law. This law transformed the 50 year-old system of examination and approval for foreign trade into a registration system; and it has made clear regulations on the import and export of goods and technology, international trade in services, the order of foreign trade and the protection of the intellectual property rights concerned with the order of foreign trade, etc, so as to accelerate its development.
Since WTO entry, China's overall level of customs duties on imports fell from 15.6 percent in 2000 to 10.6 percent in 2004. In 2005 they declined further, to 9.9 percent. Average duty on industrial products decreased to 9.3 percent, on agricultural products to 15.3 percent and on IT products under the Information Technology Agreement (ITA) of the WTO to zero. From January 1, 2006, China further reduced more than 100 import customs duties, in relation to vegetable oil, industrial chemicals, automobiles and automobile accessories.